Sea Freight in Busan Port
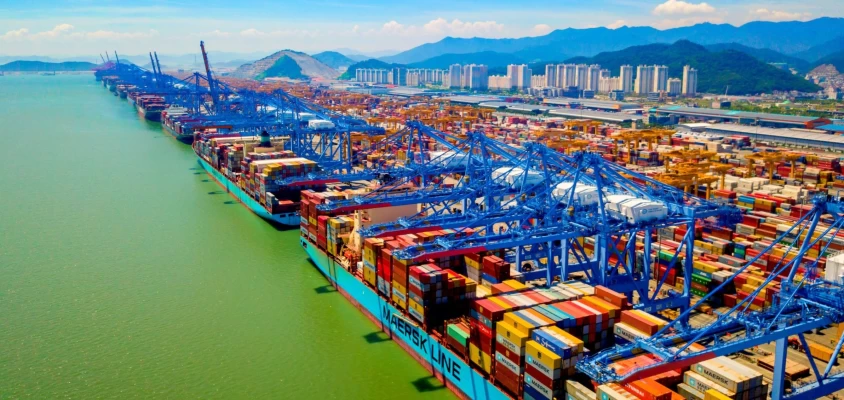
The Port of Busan, located in South Korea, is a pivotal hub in global maritime trade. As the largest port in South Korea and one of the busiest in the world, it plays a crucial role in the country’s economy and international trade. This article delves into the various aspects of sea freight operations at Busan Port, highlighting its infrastructure, services, and significance in global logistics.
Historical Background
Established in 1876, the Port of Busan has grown from a small trading port to a major international maritime center. Its strategic location at the mouth of the Nakong River, facing the Tsushima Island of Japan, has historically made it a key point for trade between Korea, China, and Japan. During the Korean War, the port was vital for receiving war materials and aid, which helped stabilize the economy.
Infrastructure and Facilities
The Port of Busan is divided into four main areas: North Port, South Port, Gam Cheon Port, and Dediego Port. Each area serves specific functions:
- North Port: Primarily handles passenger traffic and general cargo.
- South Port: Home to the Busan Cooperative Fish Market, the largest fishing base in Korea, handling 30% of the country’s marine volume.
- Gam Cheon Port: Assists in handling additional cargo volumes.
- Dediego Port: Focuses on coastal catches and smaller cargo operations.
The port boasts 10 container terminals, which collectively handled around 22 million TEU (Twenty-foot Equivalent Units) in 2019. This extensive infrastructure supports a wide range of cargo, including containers, bulk goods, and specialized cargo.
Technological Advancements
Busan Port is at the forefront of technological innovation in maritime logistics. The port has implemented advanced systems for container handling, tracking, and management, ensuring efficient and timely operations. Automation and digitalization are key components of the port’s strategy to enhance productivity and reduce turnaround times.
Economic Impact
The Port of Busan is a cornerstone of South Korea’s economy. It handles approximately 83% of the country’s containerized exports, making it the largest container and general cargo port in South Korea. The port’s activities are closely linked to the manufacturing sector, with 50% of Busan’s manufacturing jobs related to exports. The port’s efficiency and capacity have positioned South Korea as a significant player in global trade.
Environmental Initiatives
In recent years, the Busan Port Authority (BPA) has undertaken several initiatives to minimize the environmental impact of port operations. These include measures to reduce emissions, manage waste, and protect marine ecosystems. The BPA is committed to sustainable development and aims to balance economic growth with environmental stewardship.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, the Port of Busan aims to further expand its capacity and enhance its role as a global logistics hub. The port’s strategic location and advanced infrastructure make it well-positioned to handle increasing trade volumes and adapt to the evolving demands of international shipping. The BPA’s vision includes achieving a throughput of 30 million TEU in the coming years.
Conclusion Sea Freight in Busan Port
The Port of Busan is a vital asset to South Korea and the global maritime industry. Its rich history, robust infrastructure, and commitment to innovation and sustainability ensure its continued prominence in sea freight operations. As global trade dynamics evolve, the Port of Busan will undoubtedly remain a key player in facilitating international commerce.
If you have any specific questions or need more details on a particular aspect of Busan Port, feel free to ask!