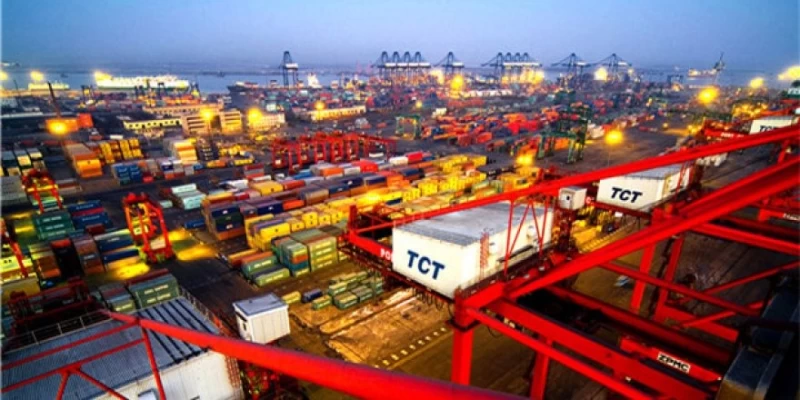
Sea Freight in the Port of Tianjin
The Port of Tianjin, located on the western shore of the Bohai Bay, is the largest port in Northern China and serves as the primary maritime gateway to Beijing. Known for its strategic location and extensive facilities, the port plays a crucial role in global sea freight, connecting China to over 800 ports in more than 200 countries and regions.
Historical Background
The port’s history dates back to 1860 when it was initially established as the Port of Tanggu. It was later reopened as Tianjin Xingang in 1952. Over the decades, the port has undergone significant expansions and modernization, transforming into one of the largest man-made ports in the world.
Infrastructure and Facilities
The Port of Tianjin covers an area of 121 square kilometers with over 31.9 kilometers of quay shoreline. It boasts 192 berths, 128 of which can accommodate vessels weighing over 10,000 tons. The port is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities, including specialized terminals for containers, bulk cargo, and liquid cargo. It also features advanced logistics and warehousing services, ensuring efficient handling and storage of goods.
Cargo Handling and Throughput
Tianjin Port is renowned for its impressive cargo handling capabilities. In 2013, the port handled 500 million tones of cargo and 13 million TEU (Twenty-foot Equivalent Units) of containers, making it the world’s fourth-largest port by throughput tonnage and ninth in container throughput. The port’s extensive network of 133 cargo routes facilitates trade with a vast array of international destinations.
Sea Freight Services
The port offers a wide range of sea freight services, catering to various shipping needs. These include Full Container Load (FCL) and Less than Container Load (LCL) shipments, providing flexibility for businesses of all sizes. The port’s efficient operations and strategic location make it an ideal hub for both import and export activities.
Economic Impact
As a major economic driver, the Port of Tianjin significantly contributes to the regional and national economy. It is a key component of the Binhai New Area, a special economic zone aimed at boosting development in Northern China. The port’s activities generate substantial revenue and employment opportunities, further enhancing its economic importance.
Environmental Initiatives
In recent years, the Port of Tianjin has implemented various environmental initiatives to minimize its ecological footprint. These include measures to reduce emissions, improve energy efficiency, and promote sustainable practices in port operations. The port’s commitment to environmental stewardship underscores its role as a responsible global trade hub.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, the Port of Tianjin is poised for continued growth and development. Plans are underway to further expand its capacity, with a target of handling 550–600 million tones of cargo by 2025. The port’s strategic initiatives aim to enhance its competitiveness and solidify its position as a leading global maritime hub.
Conclusion Sea Freight in the Port of Tianjin
The Port of Tianjin stands as a testament to China’s maritime prowess and its pivotal role in global trade. With its extensive infrastructure, efficient operations, and strategic location, the port continues to drive economic growth and facilitate international commerce. As it embraces future challenges and opportunities, the Port of Tianjin remains a cornerstone of sea freight in the region.
If you have any specific questions or need more details about certain aspects of the Port of Tianjin, feel free to ask!